The CDC recently released its Youth Risk Behavior Survey reporting that an alarmingly high percentage of American teens, particularly girls and LGBQ+ youth, are suffering from distressing mental health symptoms. With stressors like isolation from the COVID-19 lockdowns, too much screen use, frightening news reports, increasing college pressures, increasing financial strains on families, and the compare and despair dynamics that arise from social media, kids are feeling the pressure. Child experts and advocates have called for the Biden administration to declare a youth mental health emergency and are begging schools to adopt better trauma-informed health and sex education. What are the contributors, and how can we help?
The Highlights
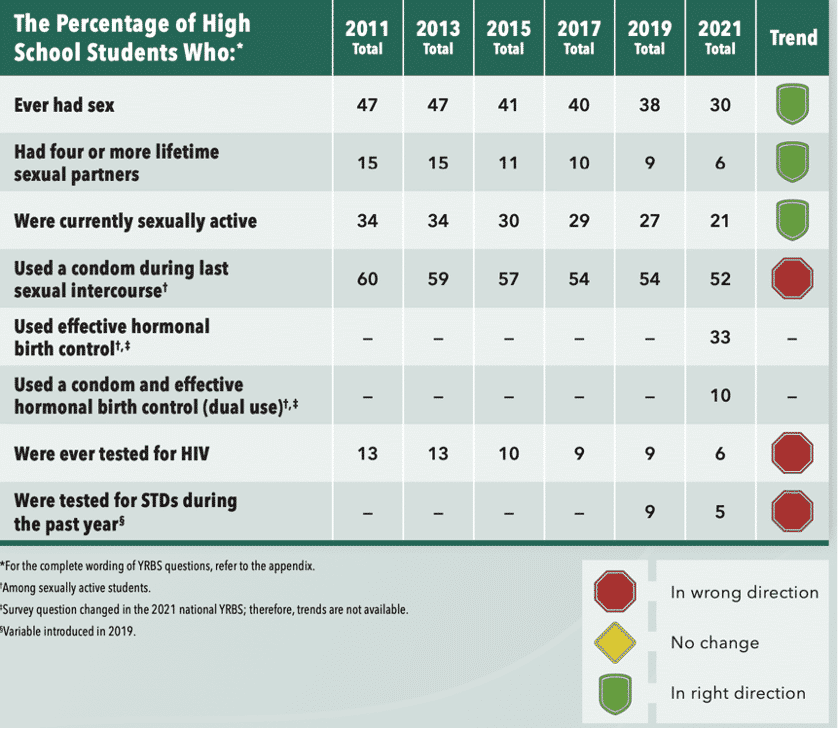
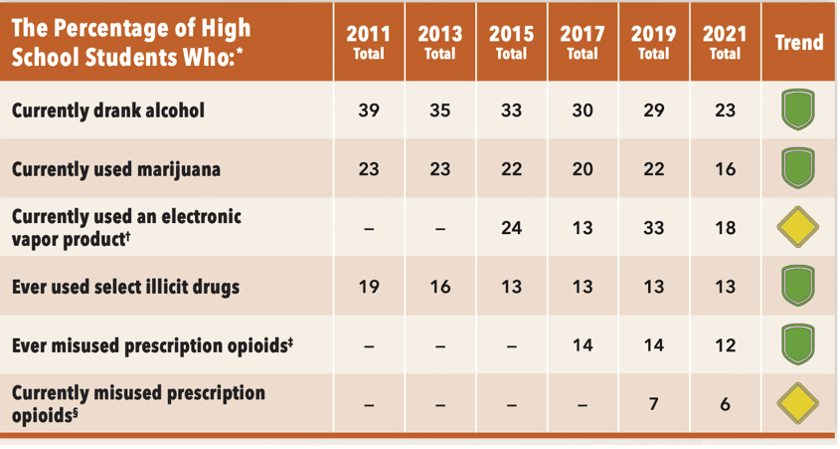
The CDC report data comes from 17,000 U.S. high school students who were surveyed in the fall of 2021 when most schools returned to in-person teaching. The good news is that overall sexual activity, substance abuse, and in-school bullying are down. The bad news is that teen safety concerns due to violence, sadness, hopelessness, and suicidality are up, especially among girls and LGBQ+ students (trans students were not identified for this survey).
Here is the Summary of Findings from The Youth Risk Behavior Survey Data Summary & Trends Report: 2011–2021
Sexual Behavior
Substance Abuse
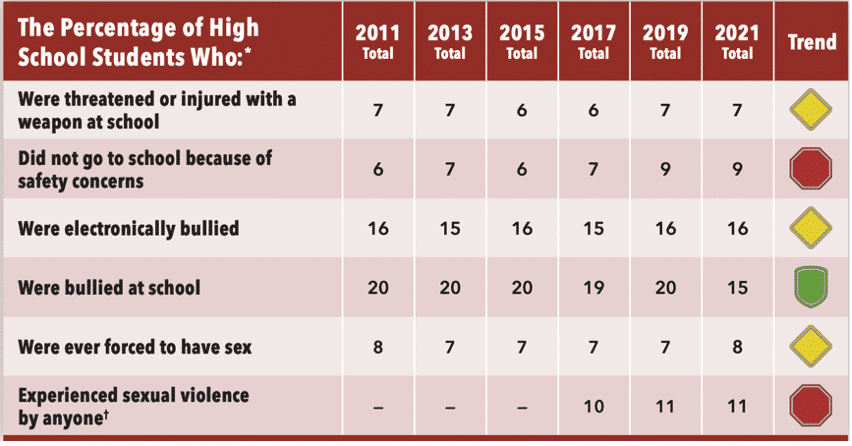
Experiencing Violence
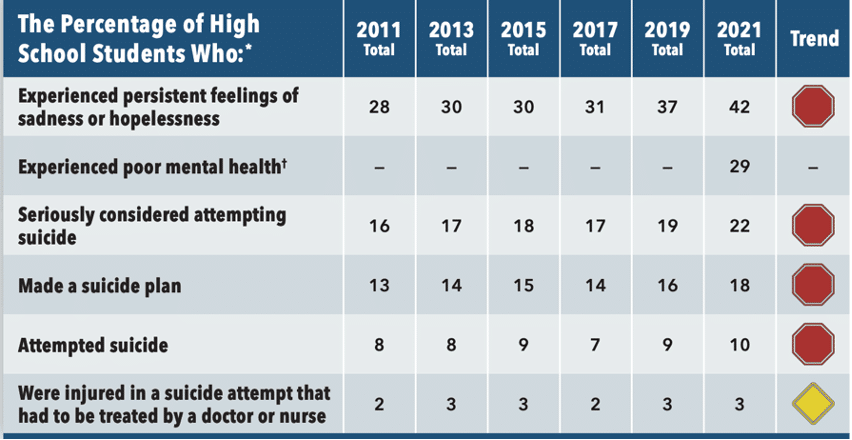
Mental Health and Suicidality
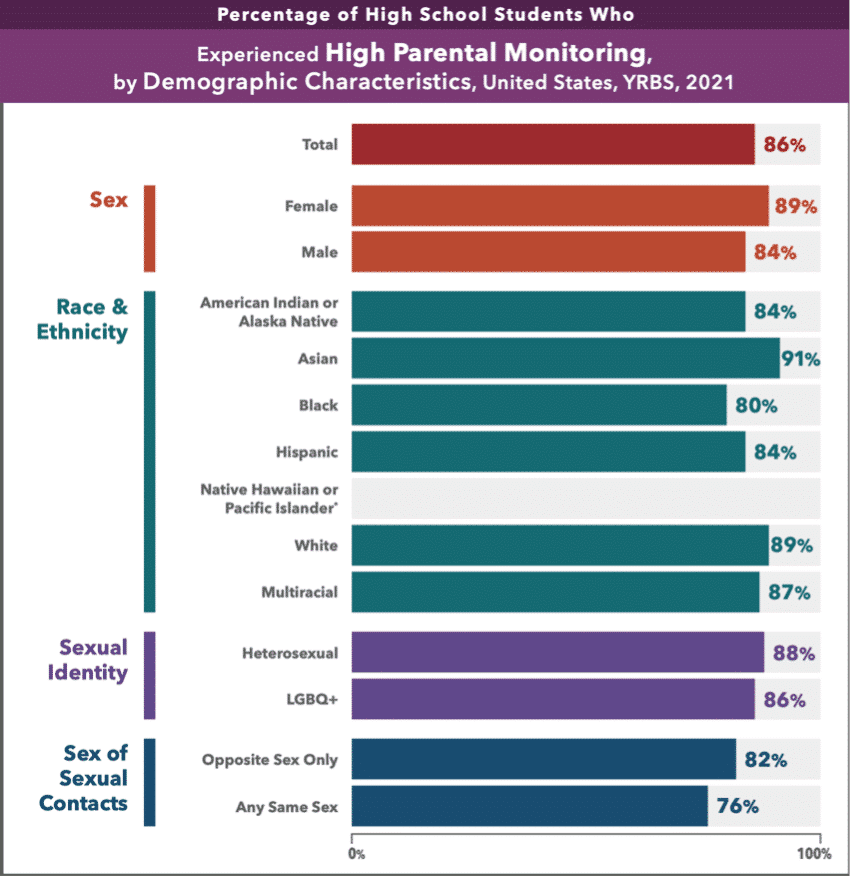
Parental Monitoring
Teen Girls
The survey suggests that nearly 3 in 5 (57%) U.S. teen girls felt so sad or hopeless that they couldn’t engage in regular activities for two weeks or more. Nearly 1 in 3 (30%) seriously considered attempting suicide—up nearly 60% from a decade ago. And 1 in 5 (18%) experienced sexual violence in the past year—up 20% since 2017.
LGBQ+ Youth
Almost 70% of LGBQ+ students said they felt persistently sad or hopeless, and 20% reported attempting suicide. Fifty-two percent of LGBQ+ teens had poor mental health symptoms in the past 30 days compared to 29% of all teens.
Possible Contributors?
It’s important to consider that the survey occurred at the end of the isolation from COVID-19. Although I am still 
We must also consider that this is a survey. Without experiments where we expose one group of teens to possible causal variables (e.g., social media or isolation) and don’t expose a control group, we can’t determine what is causing the distress.
Surveys simply state and analyze subject report. It’s impossible to tell the causes from this type of data. We are left to guess with our observations and experience, forming hypotheses and looking for evidence to support them. As the Founder of GetKidsInternetSafe, a mother, university faculty member, author, and clinician who has treated kids, teens, and families for over 25 years, I have some ideas.
PHONELY: Our kids are phonely. Because we were hunters and gatherers for 90% of human existence, our brains are wired to thrive with face-to-face tribalism. Online relationships just don’t do it for us long-term.
ISOLATION: With the isolation of COVID-19, kids lost friends and confidence and regressed in their social skills.
SOCIAL MEDIA: Social media and the internet offers a constant onslaught of online ads and marketing influencers for kids and teens. This unfiltered exposure can lead to chronic fears of being judged and ridiculed as well as feelings of inadequacy and exclusion. The CDC report demonstrates that there is an epidemic of online bullying and cybersexual violence, especially toward girls and LGBTQ youth.
PARENTING: Parenting strategies have become overly protective based on anxiety and fear resulting in less child independence and more fear of failure. Plus, they spend more time online than with us. It is difficult for parents to overcome the influence of strangers and taking away all screen activities has become nearly impossible.
NEWS: Sensational and divisive news expertly and manipulatively communicates fear-inducing trends like mass shootings, climate change, and inflation. This has got most of us rattled, especially the most vulnerable among us.
FINGER-POINTING: We have tolerated and participated in an ugly, divisive climate of entitlement, bullying, and blame rather than accountability and positive action.
GROUP-THINK: The internet speaks the language of mental health – but this may result in a group-think phenomenon of looping on mental health suffering instead of increasing agency and growth.
LACK OF APPLICABLE EDUCATION: Trauma-informed, evidence-based health and sex education isn’t being offered equitably among out schools. Parents don’t want to leave this important job to schools, but they’re also not doing a great job themselves in many instances.
NOT ENOUGH MENTAL HEALTH SERVICES: There aren’t enough mental health services available to our youth.
LACK OF FAITH AND COMMUNITY: Pulling together as a loving, cooperative team is critical for kids to feel a sense of belonging and community. As our families get smaller and we have fewer extended family to offer support, our kids are left to fend for themselves.
Of course, this is not an exhaustive list. But it does summarize much of the research findings and conjecture that has surrounded these issues. There are more ideas for the list. But for the purpose of solving the problem, how can we take these stressors into consideration as we discuss possible solutions?
Considering the complexity of the question, what can we do to improve the situation? Reverse Engineer!
Reverse engineering refers to the process of looking at possible outcomes (like the causes posited above) and slowly working backward for a solution. Although this is clearly a messy mission, I watch kids regain the mental health ground they lost every day in practice. Despite what some may think, effective psychotherapy isn’t simply listening and reflecting feelings of despair. As a cognitive-behavioral therapist, I employ techniques specifically designed to facilitate positive movement forward. I’ve found that, if I set the tone and get everybody started, parents can take it from there.
Here are some tips for improving mental health and well-being at home:
- As a family, negotiate a set of measurable goals and revisit them often for direction and motivation. Praise and reward movement forward and maintain and warm and encouraging tone along the way.
- Use storytelling and a sense of humor to normalize failure and encourage curiosity and confidence.
- Turn off the news and divisive influencers who are selling toxic ideas and products.
- Reassure kids that they are capable and loved and that grit is what matters the most, far more than being attractive or innate skills.
- Encourage kids to detox off their phones occasionally and engage more in real-life exploration and socialization.
- Stay moderate. Avoid shaming lectures and demoralizing consequences.
- Offer mindfulness, problem-solving, and communication strategies to help kids gain independence and confidence.
- Offer outcome- and science-based education that empowers informed action rather than create fear.
- Support parents in not personalizing child behaviors and help them set fair and reasonable limits with warmth, encouragement, and love.
- Lead our kids toward post-traumatic growth rather than feelings of helplessness, hopelessness, and fear with expert mentorship, fun, and opportunity.
How can GetKidsInternetSafe help?
I founded GetKidsInternetSafe so I could be part of the prevention effort – rather than just the treatment effort. If you’re not sure where to get started, we have a comprehensive suite of tools for parents, tweens and teens, educators, paraprofessionals, and professionals who work with families and kids.
- Start healthy conversations about social media use for free using our GKIS Connected Families Screen Agreement.
- Check out our agreement supplements, the Cybersecurity & Red Flags Supplement (with three tools in one) and our How to Spot Marketing Red Flags Supplement.
- Dr. Bennett’s book, Screen Time in the Mean Time, is a comprehensive and easy-to-read parenting guide for families with kids of all ages. Available on Amazon in print, e-book, and audible!
- Tighten up parental controls and monitoring with the help of our GKIS Screen Safety Toolkit. This toolkit helps to empower parents and provides them with a resource list of smart tech tools to filter, monitor, and manage online behavior.
- For families with younger kids, our home setup Connected Family Course is an awesome place to start.
- To help your tween or teen get prepared for safer internet use and social media, help prevent digital injury, and optimize wellness, check out our most popular course, the Social Media Readiness Course.
- If you need more support and accountability, sign up to work with Dr. B directly for an online parenting workshop or individual coaching.
- Want to work for screen safety as a community? We’ve thought of that too! Dr. Bennett offers live presentations and webinars for adults and kids from schools, churches, corporations, and conferences.
- If you work with kids as an educator, youth counselor, professional, or paraprofessional and want to be a go-to screen safety expert, get SCREEN SAFETY CERTIFIED! Also available for those who work with Christian families!
If you want all of our supplements and courses at a low cost for parents and kids, tweens, and teens, you’ll want our mega Screen Safety Essentials Course! This online course offers a set of four modules that will help you walk your kids through the essentials of screen safety.
I’m the mom psychologist who will help you GetKidsInternetSafe.
Onward to More Awesome Parenting,
Tracy S. Bennett, Ph.D.
Mom, Clinical Psychologist, CSUCI Adjunct Faculty
GetKidsInternetSafe.com
Photo Credits
Photo by Tim Mossholder on Unsplash